Ketogenic diet
Ketogenic diet has been around since the 1920s. It was used to control epileptic seizures in refractory seizure patients i.e. patients on which the drugs won't work.
Epilepsy is a taboo in India. It’s a problem surrounded by local myths which goes untreated for a long time (if at all!). The estimated number of persons with epilepsy in India was noted to be approximately 5.5 million, among whom approximately 4.1 million resided in rural areas (Murthy et al,1999).
What does this diet do?
1.Helps reduce the symptoms and frequency of seizures.
2.Reduce drug use and minimize side effects.
What is ketogenic diet?
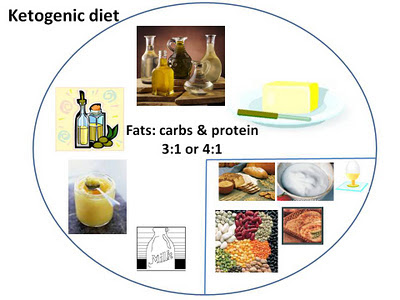
This diet replaces ketone bodies (produced by fats) as the preferred food of the brain instead of glucose(produced by carbohydrates). Therefore a person on this diet, mainly derives his/her energy from fats.
The classic ketogenic diet contains a 4:1 ratio by weight of fat to protein and carbohydrate together. It excludes high-carbohydrate foods such as starchy fruits and vegetables, bread, pasta, grains and sugar, while increasing the consumption of foods high in fat such as cream and butter
No refined carbohydrates (sugar, maida/white flour/all purpose flour, bread, candies, cakes, sweets, colas, sweetened beverages, juices etc.) or high carbohydrate foods like root vegetables (potato, sweet potato etc.), grains, pasta, rice, chapati are given to the person.
As is evident, this diet is very difficult to practice. It has been modified over the years, but the basic principle is the same. Variants of this diet are:
• MCT diet
• Low glycemic index treatment
• Modified Atkins diet
These diets allow for a more generous intake of carbohydrates and proteins than the original ketogenic diet.
Side effects
1. Side effects during the transition phase include constipation, vomitting, abdominal discomfort etc.
2. It might induce 'ketoacidosis', which if not controlled might lead to death of the patient.
3. Deficiencies of nutrients may develop so, the patient should have mineral and vitamin supplements as required.
4. Raised cholesterol levels.
Note: This diet has to be given under medical supervision. Regular tests around the initiation stage are important to know the level of ketosis maintained.
For more information:
www.epilepsy.com
Wikipedia
Matthewsfriends.org
John Hopkins Hospital
Epilepsy is a taboo in India. It’s a problem surrounded by local myths which goes untreated for a long time (if at all!). The estimated number of persons with epilepsy in India was noted to be approximately 5.5 million, among whom approximately 4.1 million resided in rural areas (Murthy et al,1999).
What does this diet do?
1.Helps reduce the symptoms and frequency of seizures.
2.Reduce drug use and minimize side effects.
What is ketogenic diet?
This diet replaces ketone bodies (produced by fats) as the preferred food of the brain instead of glucose(produced by carbohydrates). Therefore a person on this diet, mainly derives his/her energy from fats.
The classic ketogenic diet contains a 4:1 ratio by weight of fat to protein and carbohydrate together. It excludes high-carbohydrate foods such as starchy fruits and vegetables, bread, pasta, grains and sugar, while increasing the consumption of foods high in fat such as cream and butter
No refined carbohydrates (sugar, maida/white flour/all purpose flour, bread, candies, cakes, sweets, colas, sweetened beverages, juices etc.) or high carbohydrate foods like root vegetables (potato, sweet potato etc.), grains, pasta, rice, chapati are given to the person.
As is evident, this diet is very difficult to practice. It has been modified over the years, but the basic principle is the same. Variants of this diet are:
• MCT diet
• Low glycemic index treatment
• Modified Atkins diet
These diets allow for a more generous intake of carbohydrates and proteins than the original ketogenic diet.
Side effects
1. Side effects during the transition phase include constipation, vomitting, abdominal discomfort etc.
2. It might induce 'ketoacidosis', which if not controlled might lead to death of the patient.
3. Deficiencies of nutrients may develop so, the patient should have mineral and vitamin supplements as required.
4. Raised cholesterol levels.
Note: This diet has to be given under medical supervision. Regular tests around the initiation stage are important to know the level of ketosis maintained.
For more information:
www.epilepsy.com
Wikipedia
Matthewsfriends.org
John Hopkins Hospital



Comments
Post a Comment